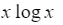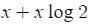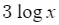티스토리 뷰
힙을 활용하는 문제긴 한데 힙이 하나도 기억 안나서 일단 내 방식으로 풀었다.
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
bool cmp(int a, int b) {
if(a == -1)
return a > b;
else if(b == -1)
return a > b;
else
return a < b;
}
int solution(vector<int> scoville, int K) {
int answer = 0;
sort(scoville.begin(),scoville.end(),cmp);
while((scoville[0] < K || scoville[1] < K) && scoville[1] != -1) {
scoville[1] = scoville[0] + scoville[1] * 2;
scoville[0] = -1;
sort(scoville.begin(),scoville.end(),cmp);
answer++;
}
if(scoville[0] < K)
return -1;
return answer;
}진짜 말그대로 단순한 코드로 짰다.
scoville을 오름차순 정렬하고 [0] [1] 을 섞어서 새 음식을 만들고 정렬하고 반복.
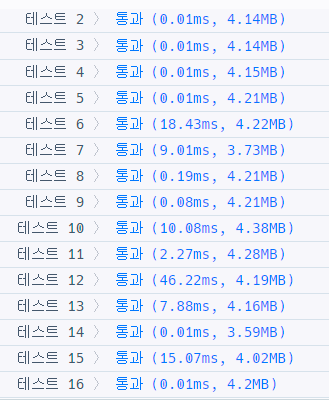
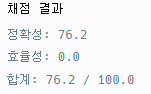
직관적이고 쉽게 정확도를 달성할 수 있었지만, 효율성이 꽝일수밖에 없다.
sort 대신 partial_sort로 맨 앞 2개만 정렬하는 방법이 있는데,
그러려면 기존 값을 -1로 바꾸어 연산 예외값으로 처리하던게 망가져서 고민이다.
아니면 아예 해당 원소를 erase하는 방법+partial_sort가 있는데 원소 제거 연산이 더 오래걸리는건 아닐지 걱정스러워서..
일단 코드를 짜보기로 했다.
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int solution(vector<int> scoville, int K) {
int answer = 0;
partial_sort(scoville.begin(),scoville.begin()+2,scoville.end());
while(scoville[0] < K || scoville[1] < K) {
scoville[1] = scoville[0] + scoville[1] * 2;
scoville.erase(scoville.begin());
answer++;
if(scoville.size() == 1)
break;
partial_sort(scoville.begin(),scoville.begin()+2,scoville.end());
}
if(scoville[0] < K)
return -1;
return answer;
}size가 1이 되는경우 루프를 나오게 하고, 0값이 k보다 작다면 -1을 내보내게 한다.
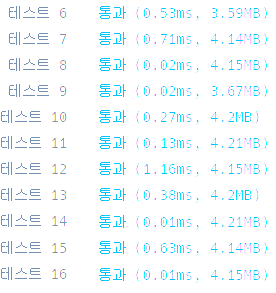
확실히 성능 향상이 두드러졌지만.. 여전히 효율성 케이스는 하나도 통과하지 못한다.
보통 효율성을 이렇게 통과 못하는거면 다른 자료구조를 채택해야 한다.
그래서, 힙 공부를 해봤다.
https://getcomponent.tistory.com/128
힙(Heap)에 대한 간략정리
완전이진트리 구조에 키값 관련 조건이 있는 자료구조. 완전이진트리? 마지막 레벨을 제외한 모든 노드는 완전히 채워져있으며, 마지막 레벨의 노드는 가능한 좌측부터 시작하는 구조 키 값 관
getcomponent.tistory.com
priority queue를 적용시켜서 문제를 다시 풀어보았다.
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int solution(vector<int> scoville, int K) {
int answer = 0;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> pq(scoville.begin(),scoville.end());
while(pq.top() < K && pq.size() > 1) {
int a = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int b = pq.top();
pq.pop();
pq.push(a+b*2);
answer++;
}
if(pq.top() < K)
return -1;
return answer;
}while 문 내에서 pop을 2개 하고, 새로운 음식을 만든 다음 다시 pq에 넣어주고 answer를 +1시키는 것을 반복한다.
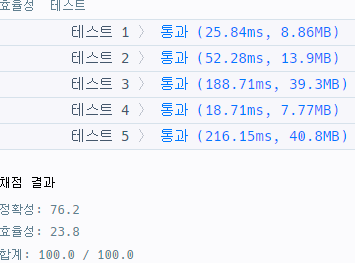
통과!

궁금한 점 해소하기
그렇다면, 왜! 이 문제에서는 partial_sort보다 priority_queue가 더 효율성이 좋았던 것일까?
| while문 내 핵심 연산 | 효율성 | |
| 1번 코드(sort) | sort(begin,end,cmp) | |
| 2번 코드(partial_sort) | erase(begin) + partial_sort 2자리 | |
| 3번 코드(priority_queue) | pop 2번 + push 1번 |
설명
1. sort 함수는 intro sort인데, quick sort 기반으로 heap sort 및 insertion sort로 보완한 sort이다. 평균 nlogn
2. partial sort는 nlogk(k는 정렬 개수, 이 문제의 경우 2)
erase로 초기값을 지우는 경우 이후 모든 값을 정렬함(매우 비효율적)으로 n
3. priority queue의 push and pop 연산은 level만큼의 비교 및 swap으로 이루어지므로 각각 logn
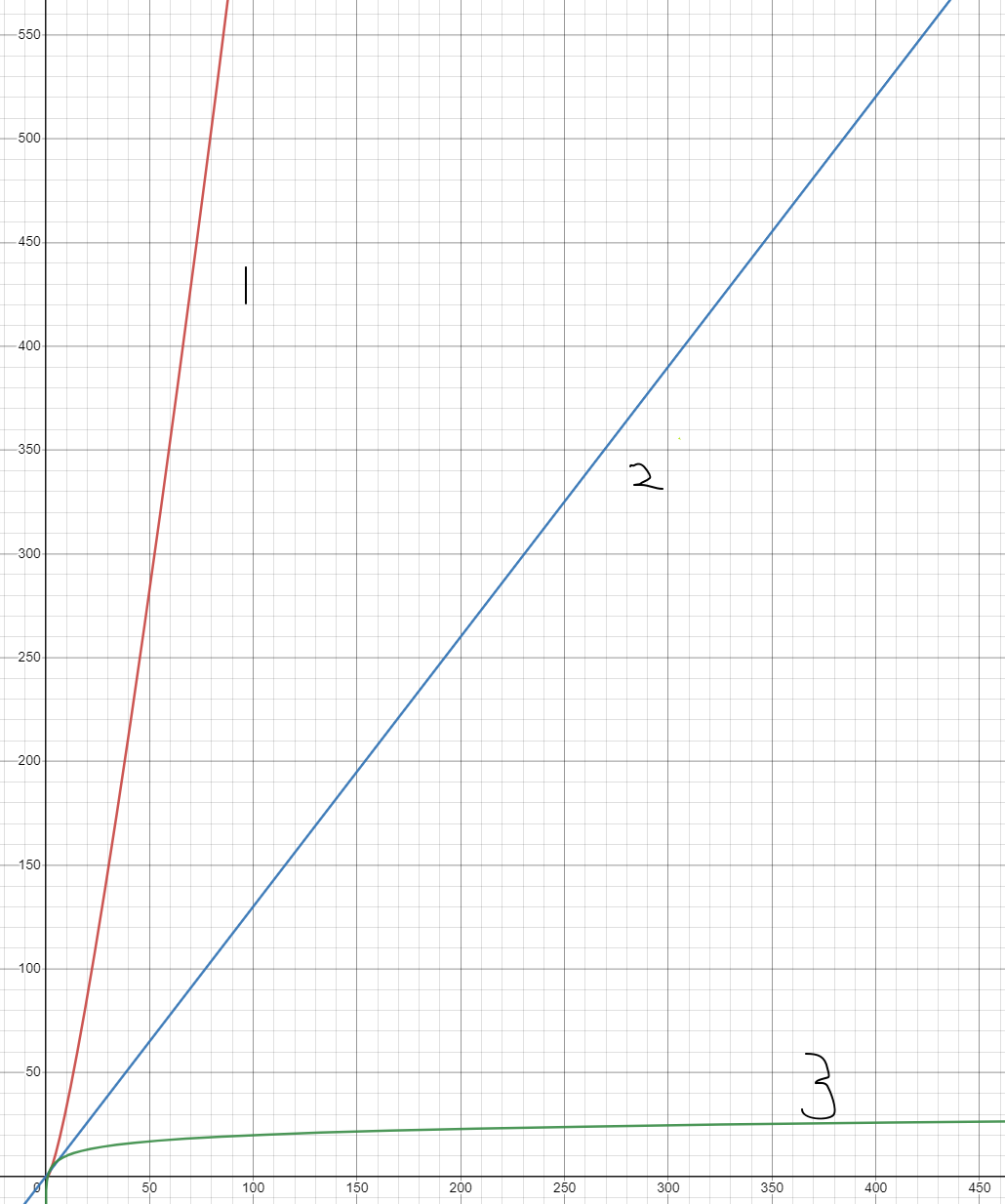

엄청난 차이를 보여준다.
1회성 정렬이 아니라, 그 자료구조에서의 push and pop, 그리고 이후 재정렬이 자주 발생한다면
priority queue를 채택하는 게 좋겠다.
'■ 알고리즘 > ◻ Programmers' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++] 다리를 지나는 트럭 (0) | 2023.01.05 |
|---|---|
| [C++] 프린터 (0) | 2022.11.26 |
| [C++]게임 맵 최단거리 (0) | 2022.11.21 |
| [C++] 네트워크 (0) | 2022.11.15 |
| [C++] 타겟 넘버 (0) | 2022.11.15 |